


Appropriate Fertilizer Use
Appropriate Fertilizer Use The goal of applying fertilizer is to supply just enough to meet the needs of the plant. Too much fertilizer can run off into nearby waters, leach into groundwater or encourage weeds. A plant’s health should be the guide. If plants suffer...
Use Compost
Use Compost The same natural recycling that happens every day in nature is at work in a compost pile. Decomposition can take years in nature, but when you compost, you give fungi, bacteria and nature’s other decomposers everything they need to recycle much faster. A...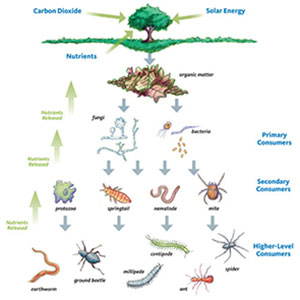
Support the Soil Food Web
Support the Soil Food Web The soil food web is the key to fertile soil. Plants are the producers — they use the sun’s energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into plant material via photosynthesis. The primary consumers or decomposers, mainly fungi and bacteria,...
Restore Compacted Soils
Restore Compacted Soils Healthy soil typically is more than 40 percent pore space, with large pores that promote drainage and small pores which help store water. This combination enables air and water to penetrate, promotes good drainage, and allows soil organisms to...

