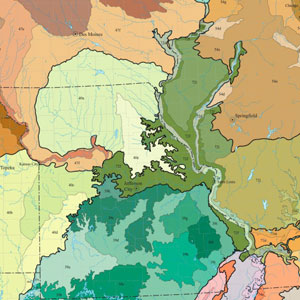
Find plants native to your ecoregion:
Wildflower Center Native Plant Database
NWF Native Plant Finder
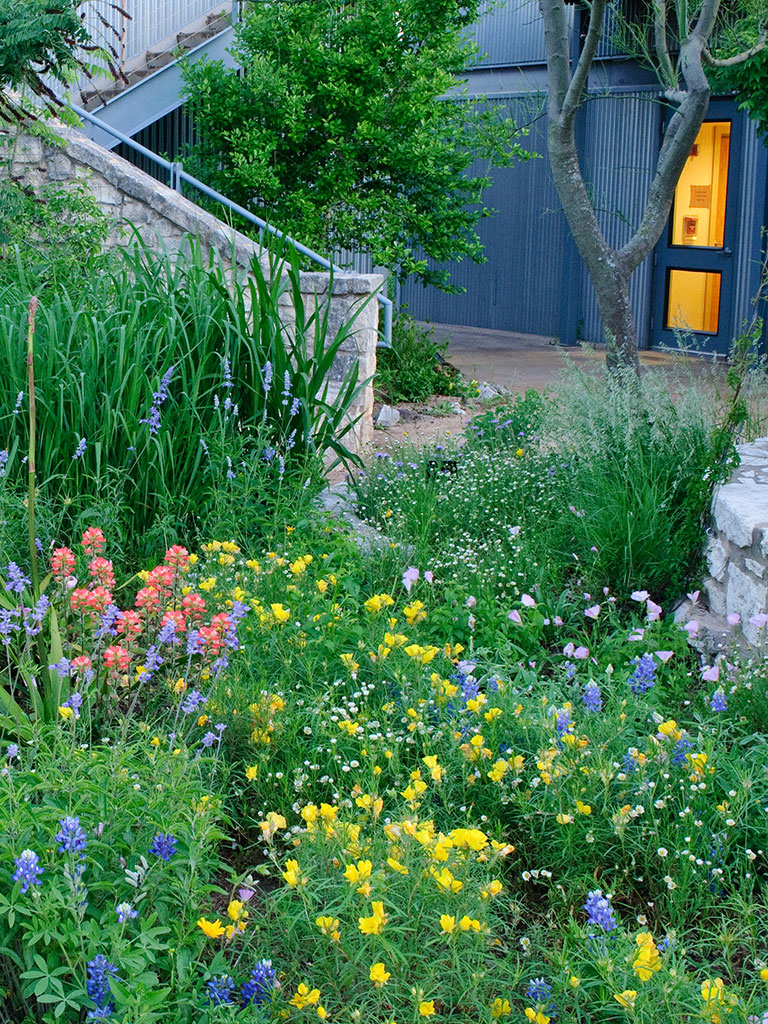

Native plants provide seasonal beauty, support wildlife and conserve water. Image credit: Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center
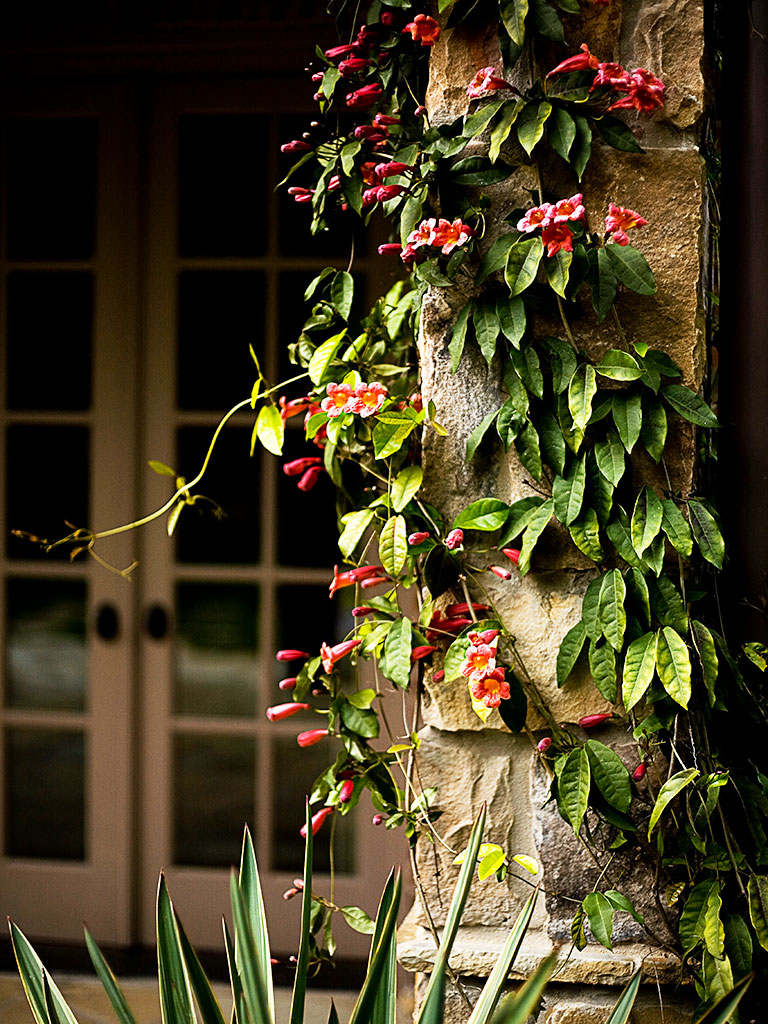

Climbing plants like this crossvine embellish architectural structures that might otherwise look stark. Image credit: Landscape For Life
Plants play an integral role in Earth’s major biogeochemical cycles, including the hydrologic, nitrogen and carbon cycles, and they provide such ecosystem services as:
- Mitigating the urban heat island effect – plants cool the air by providing shade and evaporating soil moisture.
- Cleansing air and water – vegetation absorbs, sequesters and breaks down pollutants in air and water.
- Providing oxygen – through the process of photosynthesis, vegetation takes in CO2 and releases oxygen.
- Controlling erosion – plants reduce the intensity of rainfall hitting the ground, increase the absorption of water into the soil and help hold soil together.
- Providing habitat – vegetation provides refuge, breeding and nursery habitat for wildlife above and below the ground.
- Producing resources – plants provide food and renewable non-food products such as wood, cloth fibers, oils, fruits and vegetables.
- Creating restful and peaceful settings – trees and other vegetation create places that allow us to refresh our minds, relax and better manage the stress of everyday life.
In any landscape, plants provide a diversity of beauty, form, texture, sights and smells and are often an attraction for a diversity of wildlife. Plants also provide a variety of environmental benefits like cleansing air and water, providing food and shading areas of intense heat.
As wilderness shrinks and and suburban acreage increases, what we plant in our home gardens is increasingly important. When the natural landscape is fragmented by roads and subdivisions, many habitats for wildlife are affected and ecosystems lose biodiversity.
Creating sustainable residential gardens and landscapes can help offset the loss of critical wildlife habitat and protect natural environmental benefits. When gardeners select appropriate plants, they can re-create the complexity of forests, prairies or deserts — whichever is appropriate — in a residential setting. This provides habitat for a surprising number of species, including songbirds and pollinators like bees and butterflies. Planting plants that are appropriate for the site conditions also reduces the risk that a garden will harbor invasive species, which cause billions of dollars of annual damage nationally and threaten the loss of important environmental benefits that plants provide.
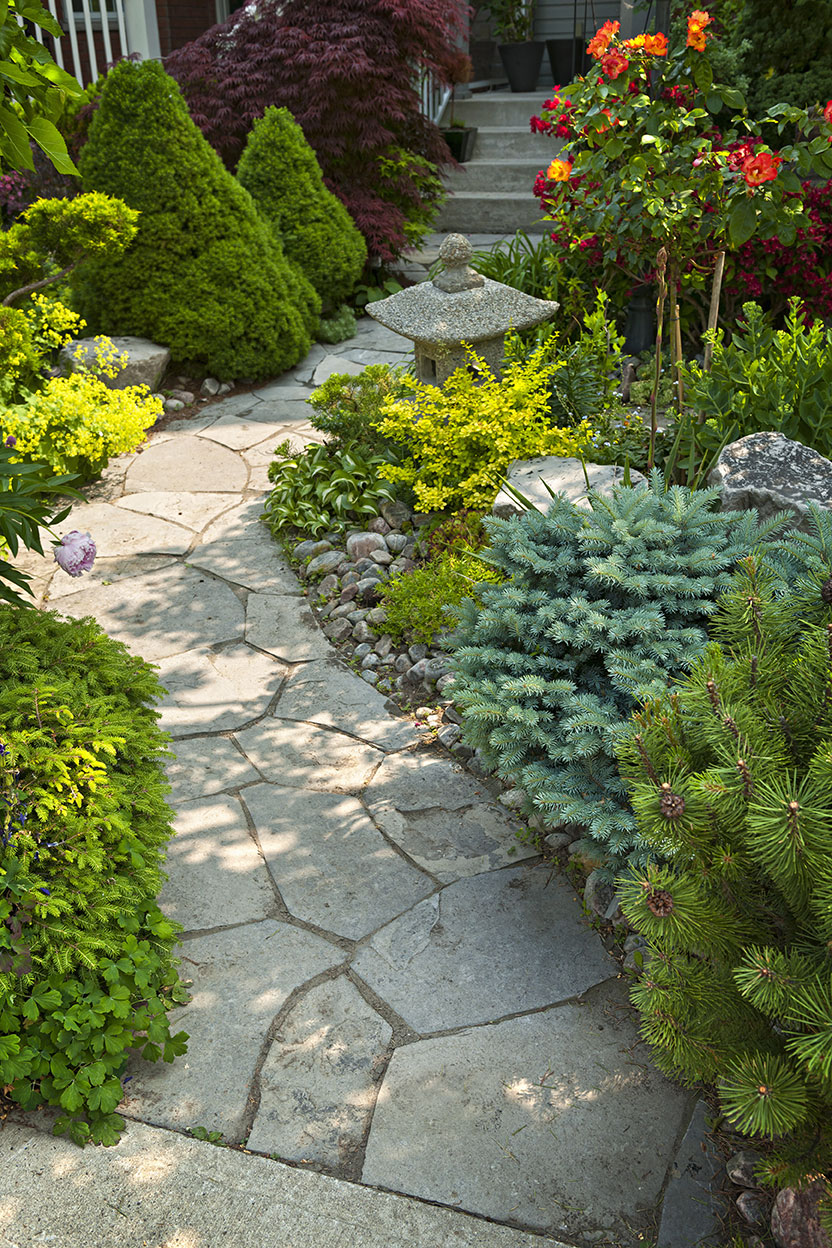

A natural flagstone path flanked by dense plantings makes for a welcoming entrance. Image credit: Shutterstock/Elena Elisseeva
Unsustainable vs. Sustainable Gardens:
How They Compare
Unsustainable Landscape
- Includes invasive plants that threaten natural ecosystems.
- Requires potable water, fertilizers and pesticides to maintain plant health.
- Often has low diversity and minimal habitat for wildlife.
- Not designed to improve home energy efficiency.
Sustainable Landscape
- Vegetation is carefully selected to avoid the use of invasive species; existing invasive species are removed from the garden.
- Includes plants that are adapted to the climate and conditions of the site.
- Includes plants that are both beautiful and serve as food or refuge for wildlife.
- Uses vegetation to reduce the heating and cooling requirements of the home and surrounding buildings.
GET STARTED WITH PLANTS

BECOME A LANDSCAPE FOR LIFE TEACHER!
Expanded training opportunities coming in 2024! Landscape For Life includes a complete kit of teaching resources which can be used to conduct classes in sustainable home gardening.
Landscape For Life™ was developed by United States Botanic Garden and the Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center, based on the principles of the Sustainable Sites Initiative (SITES®). The program is now a collaboration between Colorado State University Extension and the United States Botanic Garden.